Note:The graphical model interface is a free-form model-building interface. It is much more sophisticated than the built-in model, which means user error is more likely. It is recommended for advanced users.
To use the graphical editor to create the structural model:
•Click Edit as Graphical.
•In the displayed dialog, click Yes to confirm using the graphical editor.
•If Closed form? is currently checked, a second dialog is presented notifying the user that closed-form will not be used. This is because graphical models are built with differential equations. Click Yes to continue.
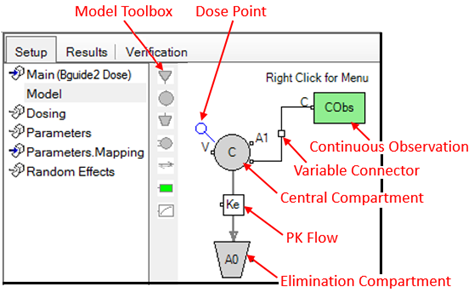
Example of a one-compartment, 1st order absorption PK model
When the graphical editor is in use, the Edit as Graphical button changes to Use Builtin. Click this button to return to the built-in model interface.
The Main Mappings, Dosing, Parameters, and Parameters.Mappings panels and all tabs except the Structure tab work the same in the Graphical model as they do in the built-in model. If no model elements are selected in the Model panel then the Structure tab displays the model parameters, statements, and scale control. Use the pointer to move the slider right or left to adjust the graphical model scale, which makes the model picture larger or smaller. If a compartment is selected, then the compartment type and type-specific settings are displayed in the Structure tab.
Users can specify the model using the Model toolbox or the right-click menu. The right-click Insert menu allows users to insert compartments, flows, observations, PD blocks, structural parameters, and other model elements. Users can also cut, copy, paste, and manipulate model elements. (The difference between Replace and Insert is that the former replaces the selected objects in the diagram with the contents of the clipboard while trying to retain wire and flow connections. The latter just copies the contents of the clipboard into the diagram.)
Insertable model elements include:
Absorption compartment ( ) (See Absorption compartment options.)
) (See Absorption compartment options.)
Central compartment ( ) (See Central compartment options.)
) (See Central compartment options.)
Peripheral compartment ( ) (See Peripheral compartment options.)
) (See Peripheral compartment options.)
Elimination compartment ( ) (See Elimination compartment options.)
) (See Elimination compartment options.)
Flow ( ) (See PK Flow.)
) (See PK Flow.)
Continuous observations ( ) (See Continuous observation block.)
) (See Continuous observation block.)
Categorical observations (See Categorical observation block.)
Event observations (See Event observation block.)
Count observations (See Count observation block.)
LL observations (See Log-likelihood observation block.)
Emax ( ) (See Emax block.)
) (See Emax block.)
Linear (See Linear block.)
Indirect (See Indirect block.)
Effect Cpt (See Effect compartment block.)
Parameter (See Parameter block.)
Procedure (See Procedure block.)
Expression (See Expression block.)
Annotation (See Annotation block.)
PBPK (See Vascular flow.)
Caution:When switching from a PK/Emax, or PK/Indirect built-in to a Graphical model, verify the tab settings. In particular, the Freeze PK? checkbox, when checked in the built-in model, can become unchecked when switching to Graphical.
