Central compartments can be connected to other PK compartments, including at least one elimination compartment (unless no drug leaves the body), by using a PK flow. Any number of central and peripheral compartments can be connected together, with one exception: if a set of PK compartments using volume parameters are connected by PK flows parameterized in microconstants, there can be only one central compartment.
-
Use the Model toolbox or select Insert > Compartment > Central from the right-click menu.
-
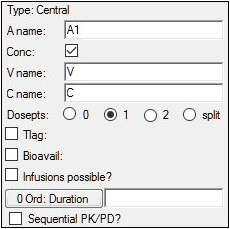
If desired, modify the default dosing variable name in the A name field.
Typically, A1 is used for intravenous input and Aa is used for extravascular input. -
Check the Conc checkbox (the default) if the compartment has concentration or volume parameters; uncheck it if there are no concentration or volume parameters.
The Conc checkbox controls the parameterization of the compartment. Selecting it adds the volume parameter V and the concentration parameter C to the model. When the checkbox is cleared, the compartment has no volume or concentration parameters, and can be useful for certain compartmental PD models. -
In the fields for the other structural parameters, enter names for each parameter.
-
Select a Dosepts option button (0, 1, 2, or split) to specify the number of dose points used by the central compartment. Select split to split dosing into the central compartment between two dosepoints.
Dose points can be defined for any PK compartment. The time(s) and amount(s) of doses are defined in the dataset. Each drug can have multiple formulations. For example, a drug can have one formulation dosing into the central compartment (IV) and another formulation dosing into an absorption compartment (oral or intramuscular). A drug model can include any number of different formulations and different drugs.
Note:Option 2 requires the dosing data to be in separate columns in the input dataset. Option split requires the data to be in the same column.
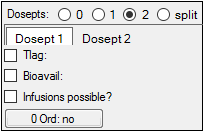
If 1, 2, or split dose points are selected, users can add time delay parameters, bioavailability expressions, add infusions, and specify zero-order absorption options. For 2 or split, these parameters can be set for each dose point by selecting the Dosept 1 and Dosept 2 tabs.
-
Check the Tlag checkbox to add a time delay parameter to the model. Enter the time lag expression in the field.
-
Check the Bioavail checkbox to measure bioavailability in the central compartment. Enter the bioavailability expression in the field.
Bioavailability expressions can be entered as a numerical value or a parameter. For example, if a user enters 0.5, half the drug goes into the compartment.
To estimate bioavailability, a parameter must be used instead of a number. For example, a user can type F (fraction of dose absorbed parameter) in the Bioavail field to estimate drug availability. If new parameter names are used in the expression, these will have to be inserted into the model. See “Parameter block” for Parameter block usage instructions.
If users want to estimate bioavailability using multiple dosing routes, then a second parameter like 1-F can be entered in the Dosept 2 tab. Using multiple dosing routes and bioavailability parameters can be useful when modeling first- and second-pass absorption rates. -
Check the Infusions possible? checkbox if the dosing uses infusions.
•A dosing parameter rate, such as Aa Rate or A1 Rate, is added to the contexts in the Main Mappings panel.
•A Duration? checkbox is also added in the Structure tab. Checking this box causes the context A1 or Aa Rate to change to A1 or Aa Duration.
-
Click 0 Ord: No multiple times to toggle through the zero-order options:
No: There is no zero-order input.
Rate: The drug is introduced into the system at a constant rate. Enter the zero-order rate expression in the field, as either a parameter or a numeric value.
Duration: The drug is introduced over a finite period of time, or duration. Enter the zero-order duration expression in the field, as either a parameter or a numeric value.
-
Select the Sequential PK/PD? checkbox if the PK model is part of a PK/PD model that is being fitted sequentially.This will freeze the PK portion of the model and turn its random effects into covariates. See “Sequential PK/PD population model fitting” for more information.
