Accumulation and Other Comparisons
AutoPilot Toolkit can run analyses to compare output from previously run NCA models. The Accumulation, Absolute Bioavailability, and Renal Clearance Comparison objects combine output from previously created NCA models to create additional report output.
The AP Accumulation, Absolute Bioavailability, and Renal Clearance Comparison objects compare output from two studies. Comparison projects use NCA output or study data that is stored locally or in Certara PKS scenarios. The NCA projects can be imported into Phoenix from a disk or loaded from PKS. If PKS is used, then all NCA output must reside in the same PKS study.
Note:There are a number of situations where comparing treatment values of differing levels between two studies can create output that may not be useful. There are also cases where such comparisons may prove valuable. The AutoPilot Toolkit does not make any assessment of when such comparisons should be done or not. For this reason, the user should be careful in the selection of the study data to be processed by the AutoPilot Toolkit’s Comparison tool, particularly when there are treatments in one study that do not appear in the other.
Use one of the following to add a Comparison object to a Workflow:
Right-click menu for a Workflow object: New > AutoPilot > AP Accumulation/Absolute Bioavailability/Renal Clearance Comparison.
Or Main menu: Insert > AutoPilot > AP Accumulation/Absolute Bioavailability/Renal Clearance Comparison.
Or right-click menu for a worksheet: Send To > AutoPilot > AP Accumulation/Absolute Bioavailability/Renal Clearance Comparison.
An AP Comparison object must have an assigned source of input data for the Reference run and at least one other Test run as a first step. If stacked data is being used, then only one input data source is needed. When the input sources are selected, AutoPilot Toolkit then creates the AP Comparison interface based on the input data.
When connected to an NCA object, the AP Comparison object detects any changes to the NCA model and generates an alert. The AP Comparison object does not correct the problem. It only alerts users that changes were detected. Users must revert their NCA changes or make the necessary changes to the AP Comparison object.
The Send To command cannot be used to map data to the Test inputs. The Select source button or the Diagram tab must be used to map data to the Test inputs. The Input checkboxes in the Setup tab are also a quick way to map/unmap sources to the reference and various tests.
To change a source of input data
The source of the input data for an Comparison object can be changed by simply remapping the input to the new source. AutoPilot Toolkit will check the compatibility of the new source’s study variables with the variables in the Comparison object’s original dataset.
-
If the new source appears to be compatible with the Comparison object, a message to this effect is presented in a dialog along with a reminder to review the object’s settings.
-
If the new source is incompatible with the Comparison object (e.g., the object, initially connected to a plasma NCA model is remapped to a urine model), a warning is generated. Continuing with mapping of the incompatible data source to the Comparison object will result in all settings and/or previous results being cleared.
This section contains the following topics:
•Stratification/Normalization tab
See also:
•“PK Comparison tables” for a listing of tables available for each combination of study design, dosing, regimen, and matrix.
•“PK Comparison graphs” for a listing of graphs available for each combination of study design, dosing, and matrix.
•“PK Comparison appendix output” for a listing of appendices available for each study design.
The differences between the three Accumulation, Absolute Bioavailability, and Renal Clearance comparison types are outlined below.
|
Comparison Type |
Input Data Requirements |
Output |
|
Accumulation |
•Both datasets must be either stacked or unstacked. •Same analyte must be compared between the two datasets. •NCA Models 200–202a •Runs must use same matrix and route. •Reference input data must be from a single-dose NCA model. •Test input data must be from a multiple-dose NCA model. |
•Overlaid time-concentration graphs •Calculation of additional parameters such as Accumulation (RA) and Linearity (LI). Comparisons are between the single-dose day and a multi-dose day, but not between two multi-dose days. |
|
Absolute Bioavailability |
•Both datasets must be either stacked or unstacked. •Same analyte must be compared between the two datasets. •Study design type must be Crossover. •NCA Models 200–202a •Runs must use same matrix and regimen. •Reference input data must be from a non-extravascular route containing one Treatment, which is either IV Bolus (model 201) or IV Infusion (model 202). •Test input data must be from an extravascular route (model 200) and can have multiple Treatments. |
•Overlaid time-concentration graphs •Calculation of additional parameters such as Absolute Bioavailability (F). •Calculation of ratios for PK parameters. •If route information is unavailable from the reference and test studies, the text strings “IV” and “Ext” will be used in legends or X-axis levels as appropriate. |
|
Renal Clearance |
•Both datasets must be either stacked or unstacked. •Same analyte must be compared between the two datasets. •NCA Models 200–212a •Runs must use the same route and regimen. •Reference input data must be from a non-urine-based matrix (model 200–202). •Test input data must be from a urine-based matrix (model 210–212). •For renal clearance calculation, the urine and blood draw collection intervals must be the same. |
•Calculation of additional parameters such as Renal Clearance (CLr=Ae/AUClast). •Calculation of ratios for PK parameters. |
|
aEach NCA model whose output is being compared must be of the same study design type. For PKS studies, all NCA output must reside in the same PKS study. Additionally, only one NCA model is required for any comparison if stacked data is used. For non-stacked comparisons, two NCA models are required. |
Note:Phoenix does not allow users to select steady state dosing for urine models. AutoPilot Toolkit uses the steady state flag to distinguish between SD (single dose) and MD (multiple dose) regimens. Therefore, AutoPilot Toolkit considers a urine study to be MD or steady state if Day is used as a Sort Variable and SD if Day is not used as a Sort Variable.
The Setup tab consists of two areas, a hierarchical listing consisting primarily of output types available for the AP Analyte Comparison object selected in the Object Browser, and a panel area for displaying options specific to an item selected in the hierarchical list.
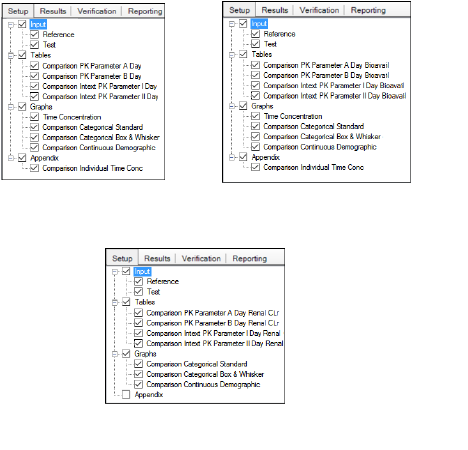
Setup tab for Accumulation, Absolute Bioavailability, and Renal Clearance Comparison objects
The Input list will vary depending on whether a stacked or unstacked data source was mapped to the Reference item. Test data inputs are not available if a stacked dataset is used as the reference.
To identify types of output:
-
Check/clear the checkbox beside a table type to include/exclude the table in the output.
-
Check/clear the checkbox beside the main Tables, Graphs, or Appendix items to add or remove all items under that heading from the output.
Note:Selecting Tables in the hierarchical list is only possible when stratifications or exclusions are set, or when the input data is stacked by analyte.
-
To set options for an output type, click the name of the output type in the hierarchical list and make changes to the options displayed in the panel on the right.
When an AP Comparison object is inserted into a project, the input source(s) must be assigned before the object can be used or modifications to object settings can be made. The input source can be mapped to NCA Final Parameters worksheets or observations datasets.
Note:The reference and test data sets used in a comparison must contain matching units for the variables being compared.
-
In the Setup tab, select Input in the hierarchical list.
OR
In the Diagram tab, right-click an AP Comparison object and select View Setup.
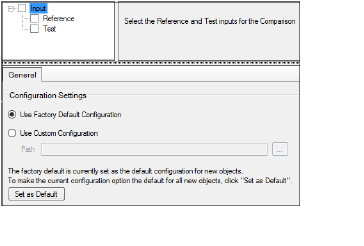
Setup tab with no input source defined
If no input sources have been defined, the options available are restricted to selecting the source and specifying an alternative source for configuration settings (refer to “General tab” for more information on configuration settings).
Users can set the variables, statistics, or precision for each table type. The options available depend on the type of table selected.
The following sections describe the table options available:
•“Variables and Statistics tabs”
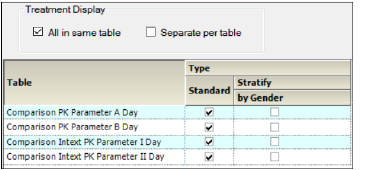
The main Tables panel shows options that can be applied when generating the tables. The options vary depending on whether stratifications are defined.
-
In the Setup tab, select Tables in the hierarchical list.
Tables panel for unstacked data
-
Check the All in Same Table box to generate a table that includes data from all treatments.
-
Check the Separate per Table box to generate a separate table for each treatment.
-
When stratification schemes have been defined, (see “Stratification/Normalization tab”) they can be applied by selecting the Stratify by ___ checkbox. Unselect the checkbox to generate only a standard table.
Tables panel for stacked data
Note:At least one stratified table must be selected if stratifications are specified or the Comparison object will not pass verification.
The Variables and Statistics tabs are formatted the same for most tables.
By default, AP Comparison output can include all PK parameters from the PK_Parameter (A – F) tables or the Intext tables and the additional parameters listed under “PK comparison parameters”.
For Absolute Bioavailability and Accumulation comparisons, the PK Parameters that are common in all NCA models are listed in the Selected list and all other parameters are listed in the Unselected list.
For Renal Clearance comparisons, since there are no common Plasma and Urine parameters, all parameters from either run are available in the comparison Unselected list.
See “PK Parameters” for a full list and descriptions of supported PK parameter study variables. See “Summary Statistics” for a full list and descriptions of supported statistics.
Note:The Variables tab may/may not be available, depending on the table type.
-
In the Setup tab, select a table type in the hierarchical list.
-
Select the Variables or the Statistics tab.
Variables and statistics that are in the Selected column will be included in the output and will be reported in the order that they appear in the column.
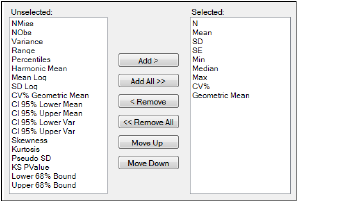
Statistics tab
The following instructions apply to both the Variables tab and the Statistics tab.
-
Select an item in one of the columns.
-
Click Add or Remove to move the item from one column to another.
-
Click Add All and Remove All to move all variables from one column to another.
-
Click Move Up and Move Down to change the position of a selected item in the list.
The Statistics tab for Intext PK Parameter tables contains different options than Statistics tabs for other tables.
-
In the Setup tab for an Intext PK Parameter type table, select the Statistics tab.
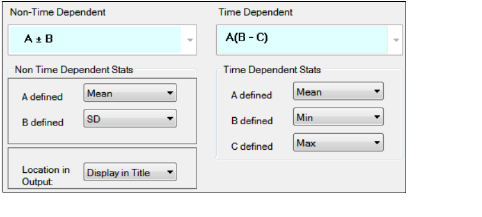
Statistics tab for intext PK parameters
-
In the Non-Time Dependent section, select the equation to be used (currently A +/- B is the only one available).
-
Identify the statistics to use in the equations from the pull-down menus.
-
Choose the location for displaying the information: Display in Title, Display in Footnote, Do not display in output.
-
In the Time Dependent section, select the equation to be used (currently A(B – C) is the only one available).
-
Identify the statistics to use in the equations from the pull-down menus.
This tab becomes available for PK Parameter tables when normalization schemes are defined (see “Stratification/Normalization tab”).
-
Select the Display option All standard, then all normalized by ____ to list all of the standard columns first, followed by normalized columns.
-
To group the columns so that the standard and normalized version of the data are together, select the Display option Group together standard and normalized by ____.
-
Toggle generation of tables with and/or without normalization for each parameter by selecting/unselecting the checkboxes in the Normalize and Standard columns.
For each variable and statistic, the precision can be set by the number of significant digits or decimal places. Selection of the type and value of numerical precision is also done through this tab.
-
In the Setup tab, select the Precision tab.
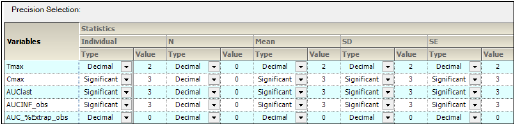
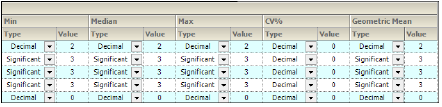
Precision tab
-
In the Type menu for each statistic, select Decimal or Significant.
-
Select a cell in the corresponding Value column to enter a new precision display value.
AutoPilot Toolkit allows the user to apply different attributes to each graph. These attributes include Y-axis scaling, summary value display, error bar display, and regression line options. Selection of PK parameters to include in the graphs is also available.
The following sections describe the graph options available for each graph type:
•“Comparison Categorical Standard panel”
•“Comparison Categorical Box & Whisker panel”
•“Continuous Demographic panel”
-
In the Setup tab, select Graphs in the hierarchical list.
Parameters that are in the Selected column will be included in the output.
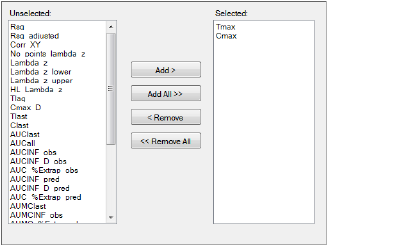
Graphs panel
-
Select an item in one of the columns.
-
Click Add or Remove to move the item from one column to another.
-
Click Add All and Remove All to move all variables from one column to another.
Time Concentration graphs are available for Absolute Bioavailability and Accumulation Comparisons, but not for Renal Clearance Comparisons.
-
In the Setup tab, select Time Concentration in the hierarchical list.
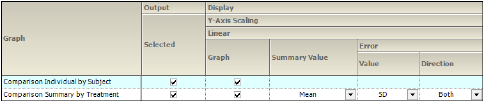
Time Concentration panel
There are two types of Table Concentration graphs available:
-
Comparison Individual by Subject: A separate graph is generated for each subject involved in the study. Each line on the graph represents a separate treatment.
-
Comparison Summary By Treatment: A single graph is generated. Each line represents a separate treatment.
The panel displays a table of options for the Time Concentration graphs, grouped into several categories and sub-categories:
Output
-
Check/Uncheck the Selected box to include/exclude a type of Time Concentration graph in the output.
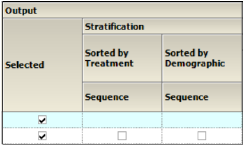
Output section of Time Concentration panel
-
When Stratification schemes have been defined (see “Stratification/Normalization tab”), they can be used either as X-axis variables in a Summary by Treatment graph type, Sorted by Treatment or Sorted by Demographic. Use the checkboxes to indicate the sorting mechanism(s) for each stratification scheme.
Display
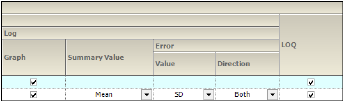
-
Graphs can be generated with a Linear or Log Y-Axis Scaling. The following options are available for both types of Y-axis scaling:
•In the Graph section, check the box to use the Y-axis scaling method. Unselect to not scale the Y-axis. Selecting this checkbox under both the Linear and Log sections will generate two graphs, one using each method.
•For Summary by Treatment type, select the Summary Value to use for plotting the summary line: Mean, Median, Geometric Mean, Harmonic Mean.
•Specify the Value (SD, SE, Variance, Min and Max, None, 68% Range) and Direction (Both, Down, Up) of error bars to display on Summary by Treatment graphs.
-
LOQ: Select the checkbox to include a regression line in the graph.
Comparison Categorical Standard panel
-
In the Setup tab, select Comparison Categorical Standard in the hierarchical list.
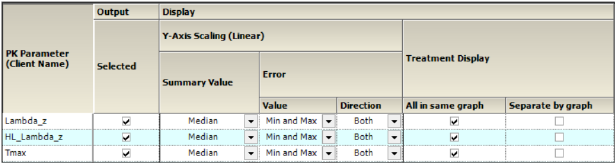
Categorical Standard panel
The PK Parameters available in the study are listed as rows in the table.
The panel displays a table of options for the Comparison Categorical Standard graphs, grouped into several categories and sub-categories:
Output
-
Check/Uncheck the Selected box to include/exclude a parameter when generating graphs.
•If normalization schemes have also been defined (see “Stratification/Normalization tab”), check/uncheck the Normalize subcategory boxes to normalize/not normalize the graphs.
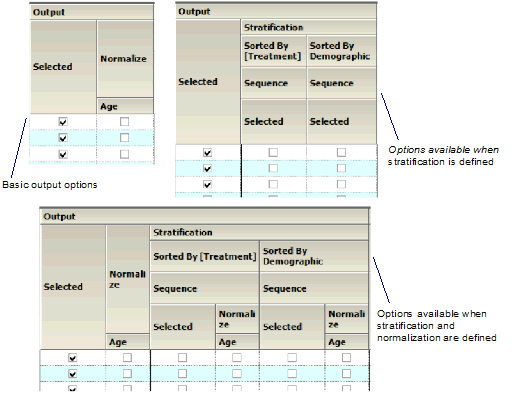
Output section of Categorical Standard panel
-
Stratification: When Stratification schemes have been defined (see “Stratification/Normalization tab”), they can be used either as X-axis variables (Sorted by [Treatment]) or new sort variables (Sorted by Demographic). Use the checkboxes to indicate the sorting mechanism(s) for each stratification scheme.
•If normalization schemes have also been defined, check/uncheck the Normalize subcategory boxes to normalize/not normalize the graphs.
Display
-
Graphs can be generated using a Linear Y-Axis Scaling. The following options are available:
•Select the statistic to use as the Summary Value when plotting the summary line: Mean, Median, Geometric Mean, Harmonic Mean.
•Specify the Value (Min and Max, Pseudo SD, SD, SE, Variance, 68% Range) of the Error bars. The only option available for Direction is Both.
•For Treatment Display, check the All in same graph box to generate a graph that includes data from all treatments. Select the Separate per graph checkbox to generate a separate graph for each treatment.
Comparison Categorical Box & Whisker panel
Note:There must be at least three subjects in the study to create Box & Whisker graphs.
-
In the Setup tab, select Comparison Categorical Box & Whisker in the hierarchical list.
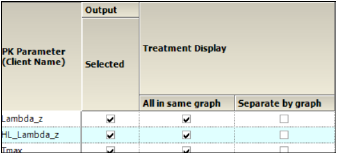
Categorical Box and Whisker panel
The PK Parameters available in the study are listed as rows in the table.
Output
-
Check/Uncheck the Selected box to include/exclude a parameter when generating graphs.
•If normalization schemes are also defined (see “Stratification/Normalization tab”), check/uncheck the Normalize subcategory boxes to normalize/not normalize the graphs.
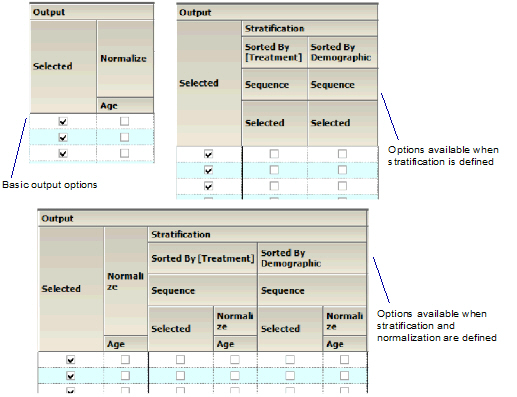
Output section of Categorical Box and Whisker panel
-
Stratification: When stratification schemes have been defined (see “Stratification/Normalization tab”), they can be used either as X-axis variables (Sorted by [Treatment]) or new sort variables (Sorted by Demographic). Use the checkboxes to indicate the sorting mechanism(s) for each stratification scheme.
•If normalization schemes have also been defined, the stratified graphs can be normalized using the Normalize subcategory checkboxes.
•Use the Selected checkboxes to produce stratified graphs that are not normalized.
Treatment Display
-
Check the All in same graph checkbox to generate a graph that includes data from all treatments.
-
Check the Separate per graph checkbox to generate a separate graph for each treatment.
-
In the Setup tab, select Comparison Continuous Demographic in the hierarchical list.
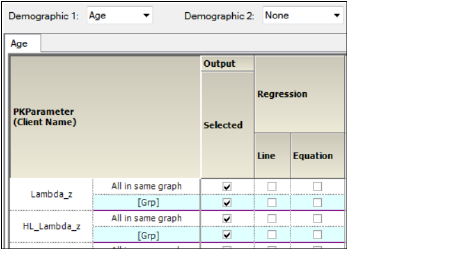
Setup tab for Continuous Demographic graphs
The panel displays a section for selecting up to two demographic(s) to use for the X-axis (Demographic 1 and Demographic 2).
When a second demographic type is selected, a second tab is created in the Comparison Continuous Demographic panel.
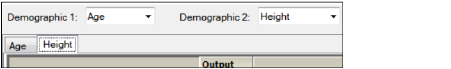
Each demographic type has its own tab in the Continuous Demographic panel
The PK Parameters available in the study are listed as rows in the table. Each parameter will have two sub-rows:
-
All in Same Graph: Sort all graphs by analyte.
-
[Grp]: Group all graphs by analyte.
The lower part of the panel contains a table of options for the Comparison Continuous Demographic graphs, grouped into several categories and sub-categories:
Output
-
Check the Selected box to create graphs for the parameter that are sorted by analyte and/or to create graphs for the parameter that are grouped by analyte. Unselect a checkbox to not generate the graph(s) for a parameter.
•If normalization schemes are also defined (see “Stratification/Normalization tab”), check/uncheck the Normalize subcategory boxes to normalize/not normalize the graphs.
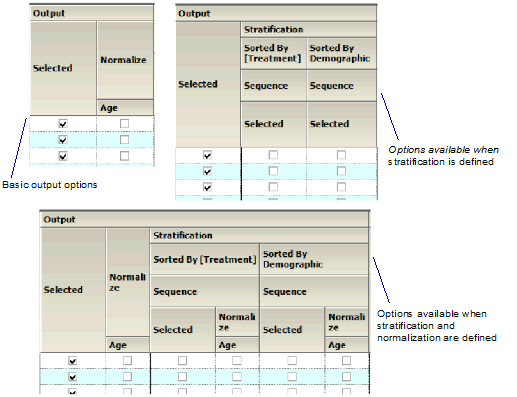
Output section of Continuous Demographic panel
-
When Stratification schemes have been defined (see Time Scale Algorithm tab), they can be used either as X-axis variables (Sorted by [Treatment]) or new sort variables (Sorted by Demographic). Use the checkboxes to indicate the sorting mechanism(s) for each stratification scheme.
•If normalization schemes have also been defined, check/uncheck the Normalize subcategory boxes to normalize/not normalize the graphs.
Regression
-
Check the Line checkbox to include a regression line in the graph.
-
Check the Equation checkbox to display the regression equation in the graph.
The General tab allows users to select the study design type, configuration settings, and whether or not to try to complete a comparison run if an error occurs.
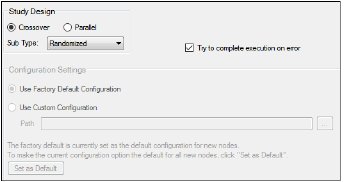
General tab in the Properties panel
The study design options in the General tab depend on the configuration settings. If the settings are changed, then the options could be different from the options listed below.
Note:The configuration settings must be specified before a dataset is mapped to the AP Comparison object.
Study Design
-
Specify that the study design type is either Crossover or Parallel.
-
For a Crossover study design, select the study SubType (Randomized, Non-Randomized, or Replicated).
-
By default, AutoPilot Toolkit tries to complete a comparison run even if errors are encountered and not all selected output can be created.
-
Unselect the Try to complete execution on error checkbox to stop a comparison run if any errors are encountered.
Configuration Settings
-
Indicate the configuration settings to use. Use Factory Default Configuration is selected by default.
-
To use customized settings, select Use Custom Configuration and click the Change Directory
 button to select the directory where the custom configuration settings file is located.
button to select the directory where the custom configuration settings file is located. -
The customized settings can be defined as the default configuration settings to use for new projects by clicking Set as Default.
Stratification/Normalization tab
The Stratification and Normalization options allow users to create additional table and/or graph output.
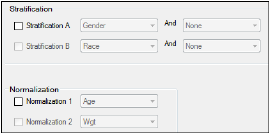
Stratification/Normalization tab in the Properties panel
Stratification
Results can be stratified (i.e., layered) using discrete demographic variables. Each stratification level can use one or two discrete demographic variables. If two variables are specified, they are associated using the logical operator AND.
Note:At least one stratified output type must be selected if stratification is enabled or the Comparison project will not pass verification.
-
To define the first level of stratification, select the Stratification A checkbox and choose the demographic variable(s) from the pull-down menu(s).
-
To define a second level of stratification, select the Stratification B checkbox and choose the variable(s) from the pull-down menu(s).
If stratifications are selected, the comparison run creates one table per stratum for the time and concentration, PK parameter, and intext PK parameter tables, using the stratification scheme as an additional group variable.
If graphs include stratification, the stratification schemes are used either as X-axis variables (sorted by treatment) or new sort variables (sorted by demographics), depending on the AutoPilot Toolkit Admin settings.
Normalization
Use the Normalization section to define normalization schemes to apply to the results. Each normalization scheme must use a different continuous demographic variable.
-
To define the first level of normalization, select the Normalization 1 checkbox and choose a demographic variable from the pull-down menu.
-
To define a second level of normalization, select the Normalization 2 checkbox and choose a variable from the pull-down menu.
AutoPilot Toolkit calculates the normalized PK parameters and includes them in the results. Users can select the PK Parameter and Intext PK Parameter tables in the hierarchical list and choose which normalized parameters to display in each table. This allows PK Parameter automation tables to include both normalized and non-normalized values.
-
Select the PK Parameter, Intext PK Parameter, PK Ratios, or PK Statistics table in the Tables node.
-
Select the Standard/Normalize tab.
-
In the Display menu, select how to display normalized PK parameters in the table output.
-
Select the Normalize checkbox beside a PK parameter to include it in the table output.
For more on using the table panels, see “Table panels”.
Column headers for the normalized variables include a normalization variable and its units. For example, oral clearance normalized by weight: CL/F/Weight (L/hr/kg). If graph output is selected that includes normalization, each normalized PK parameter is displayed in a separate graph. The Y-axis labels display the normalization in the same manner as tables.
PK parameters that are excluded from normalization are listed in “PK automation parameters”.
The Display tab contains four tabs that allow users to set output and display options, table and graph orientation, and the X- and Y-axes scaling for graphs.
The Output Options tab allows users to define exclusions, the LOQ value, and the AUC percent extrapolation threshold value.
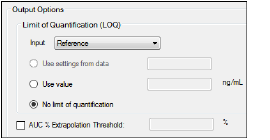
Output Options — Display tab in the Properties panel
The options for LOQ vary depending on the type of data used and the system configuration settings.
-
For unstacked data, choose one of the following methods of defining the LOQ:
•To set the LOQ value using the input data, click Use setting from data.
•To enter a value, click Use value and type a value in the corresponding field.
•Click No limit of quantification to not set an LOQ limit.
If the input dataset contains stacked data, a different LOQ can be set for each analyte.
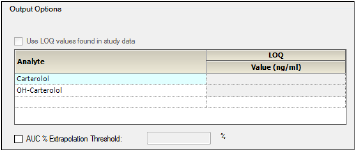
Output options for stacked data
-
For stacked input data, choose one of the following to define the LOQ value:
•Turn on the Use LOQ values found in study data checkbox to set the values for LOQ using the input data.
•Enter an LOQ value for each analyte in the Value column. (The concentration units are taken from the input dataset.)
•To not use LOQ values, turn off the Use LOQ values found in study data checkbox and leave the Value column entries blank.
Note:Setting the LOQ value for all analyts can significantly extend the execution time.
For more information, see “LOQ replacement”.
The following option is applicable to both stacked or unstacked input data:
-
Turn on the AUC% Extrapolated Threshold checkbox to use the rules for handling AUC extrapolated values that exceed the specified percentage.
See “PK parameter percent-extrapolated threshold” for details.
The Display Options tab allows users to set table and graph output display options, select the time and concentration variables in the input dataset, and choose whether or not to include data source information.
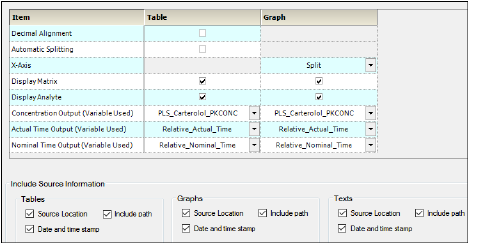
Display Options — Display tab in the Properties panel
-
Turn on the Decimal Alignment checkbox to align all values in a given column using their decimal points. See “Table data display using decimal alignment”.
-
Turn on the Automatic Splitting checkbox to allow splitting large tables across multiple pages. See “Table business rules”.
-
Select from the X-Axis pull-down if the PK parameter graphs have a Split X-axis based on individual and summary values or Offset.
-
Turn on the Display Matrix or Display Analyte checkbox to include the matrix or analyte information in the tables and/or graphs. See “Display analyte and matrix information” (tables) or “Display analyte and matrix information” (graphs).
-
Select the concentration variable to use for creating time-concentration tables and graphs from the Concentration Output (Variable Used) pull-down menu.
-
Use the Actual and Nominal Time Output (Variable Used) pull-down menus to select which data column to use for the actual and nominal times. This is set using the Admin Module. “Time Variables tab”
Through the Orientation tab, the orientation of each output item is set. A few additional settings regarding the appearance of graphs in a Word document are available for appendices involving individual time-concentration graphs.
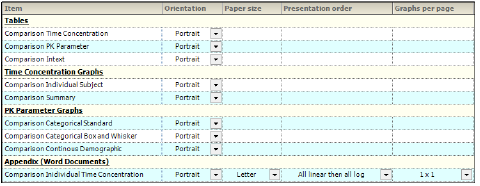
Orientation — Display tab in the Properties panel
-
In the Orientation column, select whether to position the output as a Portrait or in Landscape format from the pull-down menu for each table, graph, and appendix output.
Note:Only certain tables and graphs can be changed to Landscape. If Landscape is not supported, the Orientation setting for that table or graph defaults to Portrait and the pull-down menu is disabled.
For the Individual Time Concentration appendix output type, the following specifications can also be made:
-
Select the Paper Size as Letter or A4 from the pull-down menu.
-
Indicate the order in which the graphs are to appear using the Presentation Order column pull-down menu. Options include:
•All linear then all log: Display the linear graphs (sorted by subject) before the log graphs (sorted by subject).
•All log then all linear: Display the log graphs (sorted by subject) before the linear graphs (sorted by subject).
•Per profile, linear then log: Graphs are grouped by subject and then by analyte, with the linear graph presented before the log graph. In the output, the graphs are displayed in subject order.
•Per profile, log then linear: Graphs are grouped by subject and then by analyte, with the log graph presented before the linear graph. In the output, the graphs are displayed in subject order.
-
Specify the number of graphs per page using the pull-down in the Graphs Per Page column. Options range from 1x1 up to 4x4.
The Time Scale Algorithm tab is used to specify the scaling options for the axes, the lower and upper bounds for time scale ticks, the tick frequency, the tick units, and the maximum time scale on the X-axis. See “Time scale algorithm” for more information.
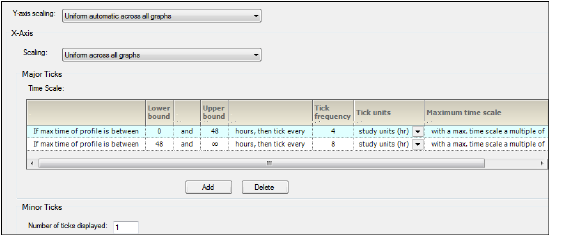
Time Scale Algorithm-Display tab in the Properties panel
-
In the Y-axis scaling menu, choose whether to scale the Y-axis uniformly across all graphs or scale the Y-axis on a per graph basis.
-
In the X-Axis area, select X-axis Scaling to be either uniformly across all graphs or on a graph by graph basis.
The Major Ticks area contains a table where each row represents a separate time scale.
-
Enter new values for lower and upper bounds in the Lower bound and Upper bound fields.
Use the Tick frequency and Tick units columns together to define the frequency with which tick marks are displayed along the X-axis.
-
Enter the value directly in the Tick frequency field and then select the units from the Tick units pull-down menu. (The default is study units, indicating that the units are derived from the study data.)
-
Set new values for the time scale multiple value in the Maximum time scale multiple value field.
-
Click Add in the Major Ticks area to add another time scale.
A new row is added to the table below the row that was selected or modified last.
-
To remove an added time scale, click in that row and then click Delete.
A minimum of two defined time scales is required.
-
In the Minor Ticks area, change the number of minor ticks displayed between the major ticks by typing a new value in the Number of ticks displayed field.
The Ordering tab is used to specify how the treatment descriptions and demographic study variables are ordered in the output.
-
In the Treatments tab, select a treatment in the list and use the Move Up and Move Down buttons to rearrange its position in the display order.
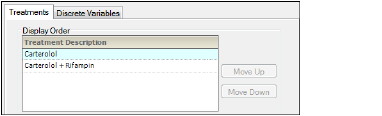
Treatments — Ordering tab in the Properties panel
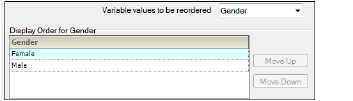
Discrete Variables — Ordering tab in the Properties panel
-
In the Discrete variables tab (available for Accumulation Comparisons), use the Variable values to be reordered menu to select different discrete study variables.
-
Select the variable in the list and use the Move Up and Move Down buttons to rearrange its position in the display order.
This tab is present only if an Accumulation, Absolute Bioavailability, or Renal Comparison project uses stacked datasets for reference and test inputs.
-
In the Analyte menu, select the analyte to use in the output.
When a stacked data PK Automation project is chosen for comparison, and an analyte comparison type is selected, users can select the analyte to be used as reference, as well as change the display order of the remaining test analytes.
-
Select an analyte in the list and use the Move Up and Move Down buttons to rearrange its position in the display order.
Caution:Do not perform any operations on the computer while the comparison run is in progress. Doing so could cause unpredictable results; keyboard and mouse input during a comparison run might affect automated AutoPilot Toolkit operations.
After the project is run, all output is arranged in groups in the Results tab.
Not all output can be viewed in Phoenix. In such cases, the right side of the Results tab will display a message with suggestions on how to view the results. One suggestion is to open an external program and load the results by clicking View in External Viewer.
AutoPilot Toolkit output can be individually exported to disk or copied to Phoenix’s Data folder. All results can be exported using AutoPilot File Explorer, which is located in the Reporting tab. For more using AutoPilot File Explorer, see “AutoPilot File Explorer”.
