The Bioequivalence object creates several output worksheets. Each type of bioequivalence model also creates a text file with model settings. If the Core Output checkbox is selected, then a Core Output text file that contains model output is added to the results.
Average bioequivalence output
Population/Individual bioequivalence output
Text output
Ratios test
-
Average Bioequivalence: Output from the bioequivalence analysis. Columns include:
Dependent: Input data column mapped to the Dependent context.
Units: Units, if specified in the input dataset.
FormVar: Input data column mapped to the Formulation context.
FormRef: Reference formulation.
RefLSM: Reference least squares mean.
RefLSM_SE: Standard error computed for reference least squares mean.
RefGeoLSM: Geometric reference least squares mean.
Test: Test formulation.
TestLSM: Test least squares mean.
TestLSM_SE: Standard error computed for test least squares mean.
TestGeoLSM: Geometric test least squares mean.
Difference: Difference between test and reference LSM values.
Diff_SE: Standard error of the difference in LSM values.
Diff_DF: Degrees of freedom for the difference in LSM values.
Ratio_%REF_: Percent ration of test LMS to reference LSM values.
(See “Least squares means” for more details.)
CI_xx_Lower(Upper): Confidence interval computations. (See “Classical intervals” for more details.)
t1_TOST: Left-tail test result.
t2_TOST: Right-tail test result.
Prob_80(125)_00: Probability results for the two one-sided t-tests.
MaxProb: Largest value of the probability results.
TotalProb: Sum of the probability results.
(See “Two one-sided t-tests” for more details.)
Power_TOST: Power of the two one-sided t-tests. (See “Power of the two one-sided t-tests procedure” for more details.)
AHpval: Anderson-Hauck test statistic. (See “Anderson-Hauck test” for more details.)
Power_80_20: Power to detect a difference in least square means equal to 20% of the reference LSM. (See “Power for 80/20 Rule” for more details.)
Prob_Eq_Var: Probability of equal variance. (See “Tests for equal variances” for more details.)
-
Ratios Test: Ratios of reference to test mean computed. One worksheet for each test formulation.
-
User Settings: User-specified settings
For convenience, the Linear Mixed Effects Modeling output is also included with Average Bioequivalence, but note that, since there is no specification of test or reference in Linear Mixed Effects Modeling, the LSM differences are computed alphabetically, which could correspond to reference minus test formulation rather than test minus reference.
-
Diagnostics: Number of observations, number of observations used, residual sums of squares, residual degrees of freedom, residual variance, restricted log likelihood, AIC, SBC, and Hessian eigenvalues
-
Final Fixed Parameters: Sort variables, dependent variable(s), units, effect level, parameter estimate, t-statistic, p-value, intervals, etc.
-
Final Variance Parameters: Final estimates of the variance parameters
-
Initial Variance Parameters: Parameter and estimates for variance parameters
-
Iteration History: Iteration, Obj_function, and column for each variance parameter
-
Least Squares Means: Sort variable(s), dependent variable(s), units, and the least squares means for the test formulation
-
LSM Differences: Difference in least squares means
-
Parameter Key: Variance parameter names assigned by Phoenix
-
Partial SS: Only for 2x2 crossover designs using the default model: ANOVA sums of squares, degrees of freedom, mean squares, F-tests and p-values for partial test
-
Partial Tests: Sort Variable(s), Dependent Variable(s), Units, Hypothesis, Hypothesis degrees of freedom, Denominator degrees of freedom, F statistic, and p-value
-
Residuals: Sort Variable(s), Dependent Variable(s), Units, and information on residual effects vs. predicted and observed effects
-
Sequential SS: Only for 2x2 crossover designs using the default model: ANOVA sums of squares, degrees of freedom, mean squares, F-tests and p-values for sequential test
-
Sequential Tests: Sort Variable(s), Dependent Variable(s), Units, Hypothesis, Hypothesis degrees of freedom, Denominator degrees of freedom, F statistic, and p-value
Population/Individual bioequivalence output
The worksheets that are created depend on which model options are selected.
-
Population Individual: Output from the bioequivalence analysis. Columns include:
Dependent: Input data column mapped to the Dependent context.
Units: Units, if specified in the input dataset.
Statistic: Name of the statistic.
Value: Computed value of the statistic.
Upper_CI: Upper bound (an upper bound < 0 indicates bioequivalence).
Conclusion: Bioequivalence conclusion.
-
Ratios Test: Ratios of reference to test mean. One worksheet for each test formulation.
-
User Settings: User-specified settings
The population/individual bioequivalence statistics include:
Difference (Delta): Difference in sample means between the test and reference formulations.
Ratio(%Ref): Ratio of the test to reference means expressed as a percent. This is compared with the percent of reference to detect that was specified by the user, to determine if bioequivalence has been shown. The ratio is expected to be 100% if both formulations are exactly equal. If the values of the two dependents are both over 100, it indicates that the test formulation resulted in higher average exposure than the reference. Values <100 indicate the reverse. For example, if the user specified a percent of reference to detect of 20%, and also specified a ln-transform, then Ratio(%Ref) needs to be in the interval (80%, 125%) to show bioequivalence for the ratio test.
See “Least squares means” for more details.
SigmaR: value that is compared with sigmaP, the Total SD Standard, to determine whether mixed scaling for population bioequivalence will use the constant-scaling values or the reference-scaling values.
SigmaWR: value that is compared with sigmaI, the Within Subject SD Standard, to determine whether mixed scaling for individual bioequivalence will use the constant-scaling values or the reference-scaling values.
See “Bioequivalence criterion” for more details.
Computed bioequivalence statistics include:
Ref_Pop_eta: Test statistic for population bioequivalence with reference scaling
Const_Pop_eta: Test statistic for population bioequivalence with constant scaling
Mixed_Pop_eta: Test statistic for population bioequivalence with mixed scaling
Ref_Indiv_eta: Test statistic for individual bioequivalence with reference scaling
Const_Indiv_eta: Test statistic for individual bioequivalence with constant scaling
Mixed_Indiv_eta: Test statistic for individual bioequivalence with mixed scaling
Because population/individual bioequivalence only allows crossover designs, the output also contains the ratios test, described under “Ratios test”.
The Bioequivalence object creates two types of text output: a Settings file that contains model settings, and an optional Core Output file. The Core Output text file is created if the Core Output checkbox is selected in the General Options tab, then the Core Output text file is created. The file contains a complete summary of the analysis, including all output as well as analysis settings and any errors that occur.
For any bioequivalence study done using a crossover design, the output also includes for each test formulation a table of differences and ratios of the original data computed individually for each subject.
Let test be the value of the dependent variable measured after administration of the test formulation for one subject. Let ref be the corresponding value for the reference formulation, for the case in which only one dependent variable measurement is made. If multiple test or reference values exist for the same subject, then let test be the mean of the values of the dependent variable measured after administration of the test formulation, and similarly for ref, except for the cases of ‘ln-transform’ and ‘log10-transform’ where the geometric mean should be used:
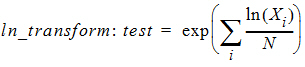

where Xi are the measurements after administration of the test formulation, and similarly for ref. For each subject, for the cases of no transform, ln-transform, or log10-transform, the ratios table contains:
Difference=test – ref
Ratio(%Ref)=100*test/ref
For data that was specified to be ‘already ln-transformed,’ these values are back-transformed to be in terms of the original data:
Difference=exp(test) – exp(ref)
Ratio(%Ref)=100*exp(test – ref)=100*exp(test)/exp(ref)
Similarly, for data that was specified to be ‘already log10-transformed’:
Difference=10test – 10ref
Ratio(%Ref)=100*10test – ref=100*10test/10ref
Note:For ‘already transformed’ input data, if the mean is used for test or ref, and the antilog of test or ref is taken above, then this is equal to the geometric mean.
