Output from the Bioequivalence module includes the classical intervals for confidence levels equal to 80, 90, 95, and for the confidence level that the user gave on the Options tab if that value is different than 80, 90, or 95. To compute the intervals, first the following values are computed using the students-t distribution, where 2*alpha=(100 – Confidence Level)/100, and Confidence Level is specified in the user interface.
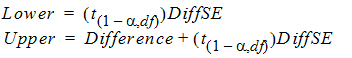
These values are included in the output for the no-transform case. These values are then transformed if necessary to be on the arithmetic scale, and translated to percentages. For ln-transform or data already ln-transformed,
CI_Lower = 100exp(Lower)
CI_Upper = 100exp(Upper)
For log10-transform or data already log10-transformed,
CI_Lower = 100 x 10Lower
CI_Upper = 100 x 10Upper
For no transform,
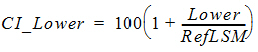
= 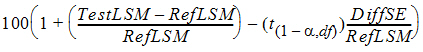
= 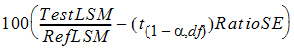
where the approximation RatioSE=DiffSE/RefLSM is used. Similarly,
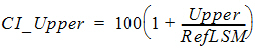
Concluding whether bioequivalence is shown depends on the user-specified values for the level and for the percent of reference to detect. These options are set on the Options tab in the Bioequivalence object. To conclude whether bioequivalence has been achieved, the CI_Lower and CI_Upper for the user-specified value of the level are compared to the following lower and upper bounds. Note that the upper bound for log10 or ln-transforms or for data already transformed is adjusted so that the bounds are symmetric on a logarithmic scale.
LowerBound
= 100 – (percentReferenceToDetect)
UpperBound (ln-transforms)
= 100 exp(–ln(1 – fractionToDetect))
= 100 (1/(1 – fractionToDetect))
UpperBound (log10-transforms)
= 100*10^(–log10(1 – fractionToDetect))
= 100 (1/(1 – fractionToDetect))
UpperBound (no transform)
= 100+(percentReferenceToDetect)
If the interval (CI_Lower, CI_Upper) is contained within LowerBound and UpperBound, average bioequivalence has been shown. If the interval (CI_Lower, CI_Upper) is completely outside the interval (LowerBound, UpperBound), average bioinequivalence has been shown. Otherwise, the module has failed to show bioequivalence or bioinequivalence.
