(Note that, since IT2S-EM does not compute standard errors, these options are not displayed if IT2S-EM is selected for the algorithm.)
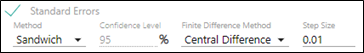
Check the Standard Errors box to perform standard error calculations based on the following settings.
Select the Method for computing the covariance matrix of parameter estimators (method availability depends on the selected algorithm):
Standard errors of parameter estimators are computed as the square roots of diagonal elements of the covariance matrix of parameter estimators. The covariance matrix is evaluated using the Hessian method and is computed as the inverse of the Hessian matrix (matrix of second-order partial derivatives) of the negative log-likelihood function with respect to estimated parameters.
Fisher Score: Evaluates the covariance matrix as the inverse of the score matrix (S), which is defined as the sum of outer product of the gradient (vector of first-order partial derivatives) of each individual’s log-likelihood function with respect to estimated parameters. The Fisher Score method is fast and robust, but less precise than the Sandwich and Hessian methods.
Hessian: The covariance matrix is the inverse of the Hessian matrix (H) of the negative log-likelihood function with respect to estimated parameters.
Sandwich: Evaluates the covariance matrix as H-1SH-1. The Sandwich method has both advantages and disadvantages relative to the Hessian method. The main advantage is that, in simple cases, the Sandwich method is robust for covariance model misspecification, but not for mean model misspecification. The main disadvantage is that it can be less efficient than the simpler Hessian method when the model is correctly specified.
Auto-detect: When selected, NLME chooses the method. Specifically, if both Hessian and Fisher score methods are successful, then it uses the Sandwich method. Otherwise, it uses either the Hessian method or the Fisher Score method, depending on which method is successful. Check the Core Status text output to see which method is used.
In the Confidence Level field, enter the confidence interval percentage.
From the Finite Difference Method menu, select the form of standard error to compute.
Central Difference: The second-order derivative of f uses the form:
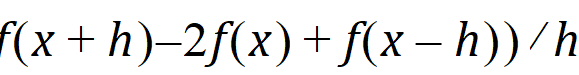
Forward Difference: The second-order derivative of f uses the form:
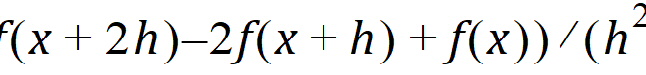
In the Step Size field, enter the relative step size to use in differentiation of log likelihood function for computation of the standard errors.
Note: Computing the standard errors for a model can be done as a separate step after model fitting. This allows reviewing of the model fitting results before spending the time computing standard errors.
For engines other than QRPEM:
– After doing a model fitting, accept all final estimates of the fitting.
– Set the number of iterations to zero.
– Rerun with a method selected for the Finite Difference Method option.
For QRPEM, use the same steps, but also request around 15 burn-in iterations.