Pirana can calculate the Akaike Information Criterion and the Bayesian Information Criterion. These criteria are defined as follows:
|
AIC = 2 · k − 2 · ln(L) |
(1) |
|
BIC = −2 · ln(L)+ k · ln(n) |
(2) |
with
k = the number of parameters in the model,
L = the maximized value of the likelihood function, and
n = the number of observations in the dataset used in fitting the model.
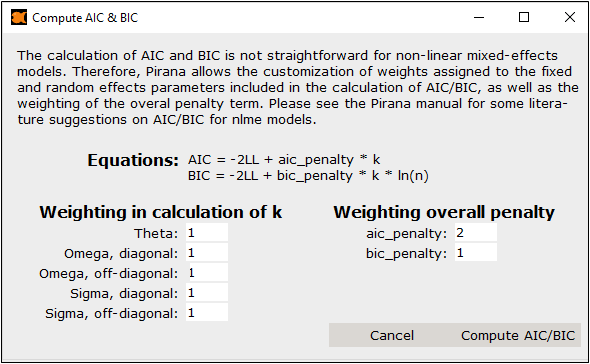
The calculation of these criteria is, however, not so straightforward for non-linear mixed-effects models, and the weights/penalties applied to parts of the equation can be different in different circumstances. Pirana allows the penalties to be changed when it calculates the AIC/BIC.
-
Select the model in the list.
-
Click
 .
.
Or
Right-click the selected model and choose Model > Comput AIC & BIC from the menu. -
Adjust the weightings and penalties for the various parts of the calculation as needed by typing directly in each field.
-
Click Compute AIC/BIC.
Some references to AIC and BIC literature are listed below.
–Vaida and Blanchard (2005). Conditional Akaike information for mixed-effects models. Biometrika 92(2): 351-370.
–Liang, et al (2008). A note on conditional aic for linear mixed-effects models. Biometrika 95(3): 773-778.
–Hodges and Sargent (2001). Counting degrees of freedom in hierarchical and other richly-parameterized models. Biometrika 88(2): 367-379.
–Donohue et al. (2011). Conditional Akaike information under generalized linear and proportional hazards mixed models. Biometrika 98(3): 685-700.
–Delattre et al. BIC selection procedures in mixed effects models http://hal.inria.fr/docs/00/69/64/35/PDF/RR-7948.pdf.
