Right-click the selected model and choose Translate model from the menu.
Or click ![]() in the toolbar.
in the toolbar.
Select the type of translation from the pop-up.
ADVAN 1-5 to $DES — Translates NM-TRAN models written in ADVAN routine (1-5) to ordinary differential equations (ODEs).
MU-referencing thetas-etas — Converts models written using normal- or log-normal hs. (See “Example 1”.)
$DES to difference equations — Translates all code written in $DES, other than the dA/dt system, to $PK and adds required code (using MTIME).
For some models written in ODEs, writing parts of the model in difference equations can reduce computational burden, while maintaining parameter precision (see Petersson, K.J., et al. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2010 Oct. 37(5):493-506).
To R: Extracts parameter estimates for the structural model (q) and the between subject variability matrix (W).
Note that a multi-dose simulation is automatically implemented (Pirana currently does not read in the dataset to extract dosing information). No residual error model is implemented in the R translators but can be added by the user.
PKPDSim — This package is not available on CRAN but may be sourced from GitHub. For example, within R, use:
library(devtools)
install_github("ronkeizer/PKPDsim")
library(PKPDsim)
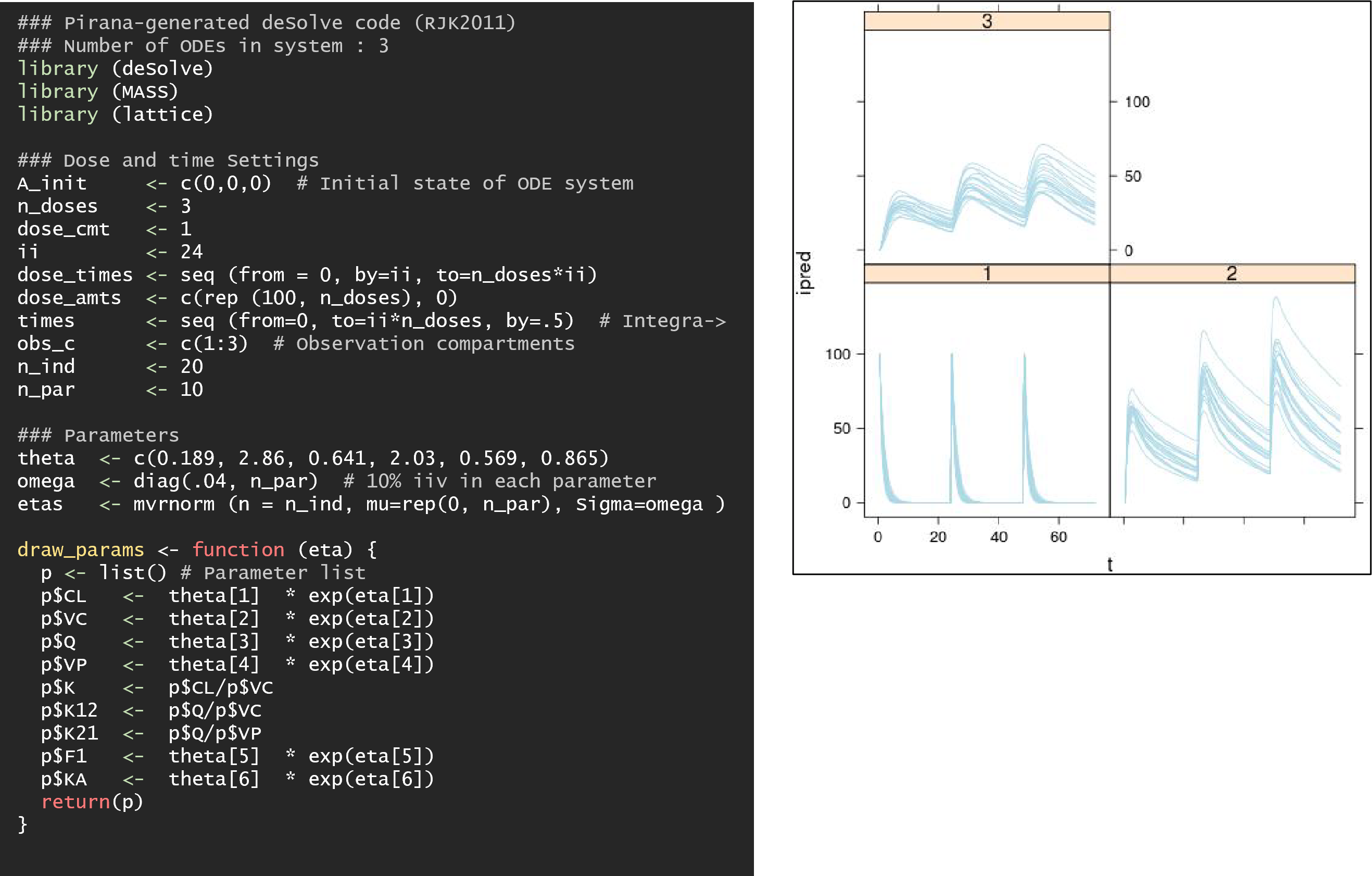
deSolve — R code generated using this option is automatically loaded in the defined R interface. (See “Example 2”.)
To Matlab: Extracts parameter estimates for the structural model (q) only.
to PopED files — Creates required files for PopED execution, allowing for evaluation of optimal study designs (OD). Design details and other optimization settings need to be provided.
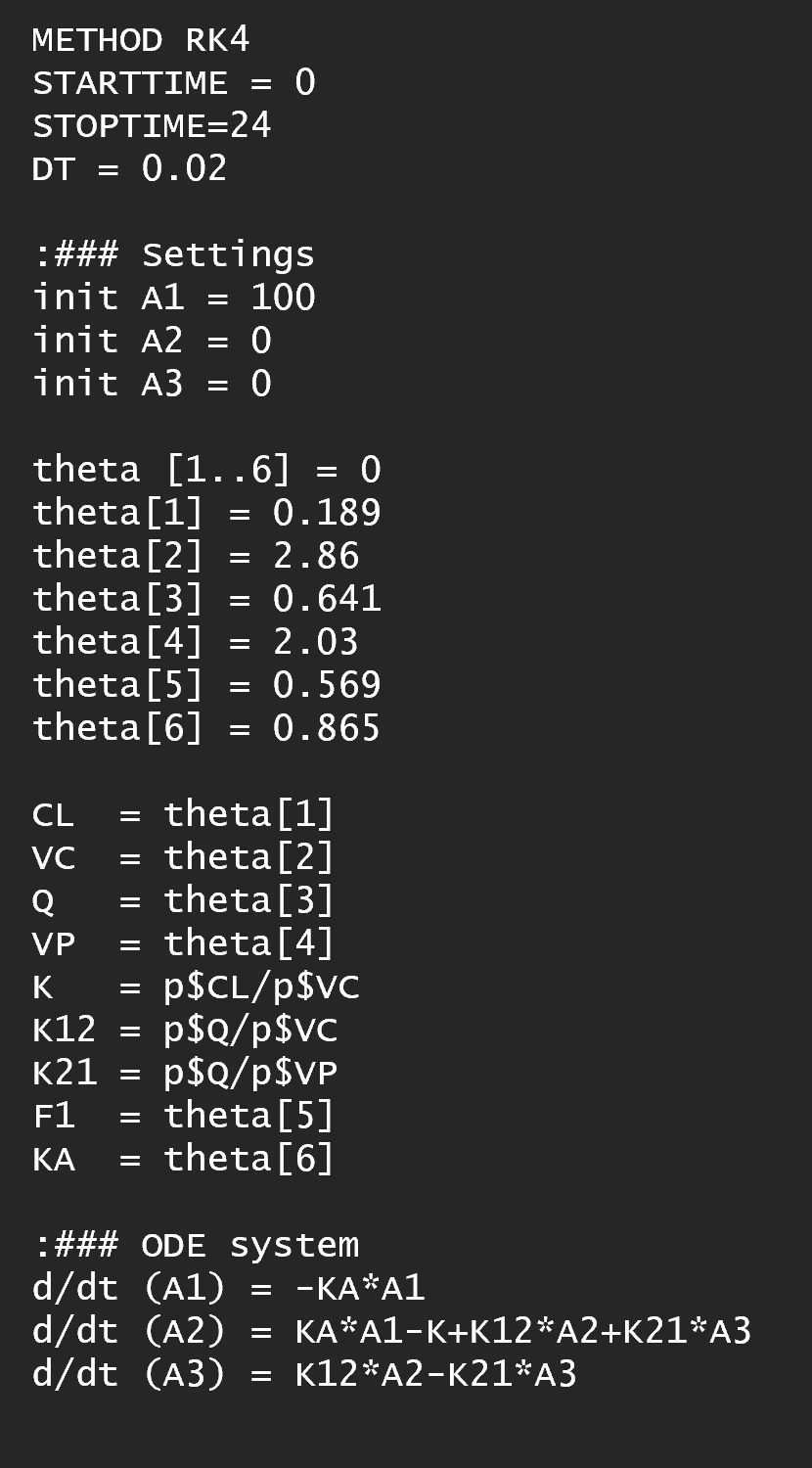
To Berkely Madonna: Extracts parameter estimates for the structural model (q) and the between subject variability matrix (W). (See “Example 3”.)
Include between-subject variability — Check to consider variability between subjects, then choose the type of sampling for the computations: Univariate sampling or Multivariate sampling.
Enter a name for the new file in the field (use ![]() to select a different location).
to select a different location).
Press Translate.
Note: For Matlab and Berkely Madonna, generated code is automatically loaded into the defined code editor.
NONMEM Mu-referencing thetas-etas conversion will take:
CL = THETA(1) * EXP(ETA(1))
and convert it into:
MU_1 = LOG(THETA(1)) ; ** MU-referenced by Pirana
CL = EXP(MU_1+ETA(1)) ;
Original equation: CL = THETA(1) * EXP(ETA(1))
An example of generated R code is depicted on the left and associated simulation output for the deSolve-generated R code on the right.
An example of generated Berkely Madonna code is depicted in the following image.