The computational formulas for area under the curve calculations are as follows. If the logarithmic trapezoidal rule fails in an interval because C1 <= 0, C2 <= 0, or C1 = C2, then the linear trapezoidal rule will apply for that interval.
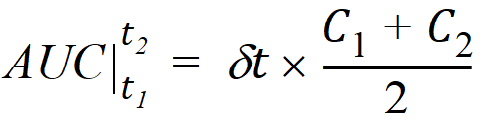
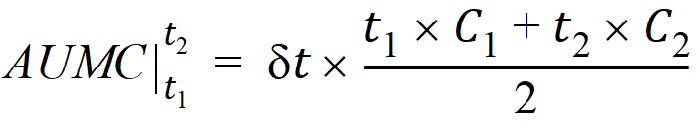
where dt is (t2 – t1).
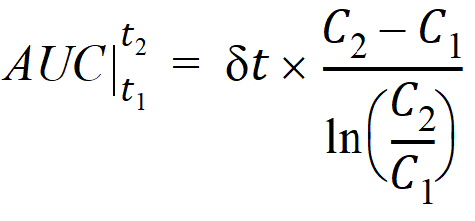
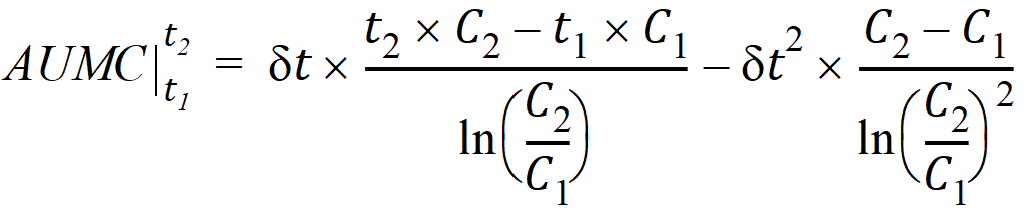
where dt is (t2 – t1).
The computational formulas for interpolating (t1, C1) and (t2, C2) to obtain C* at time t*, for t1 < t* < t2, are as follows. If the logarithmic interpolation rule fails in an interval because C1 <= 0 or C2 <= 0, then the linear interpolation rule will apply for that interval.
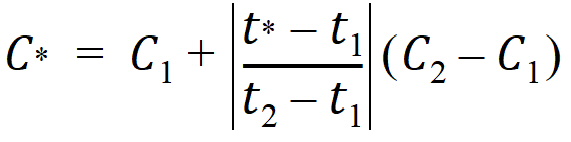
Logarithmic interpolation rule
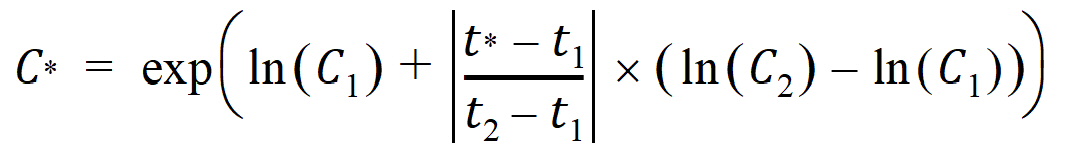
For extrapolation to find C* after the last numeric observation, see the next section.
Additional rules for plasma and urine models
For a partial area to be computed, the end time for the partial area must be greater than the start time, and both the start time and end time for the partial area must be at or after the dosing time.
Because the times for partial areas might not occur at observations, additional rules apply for interpolation, extrapolation, and AUC for plasma and urine models. For drug effect models, only interpolation applies; no extrapolations will be done outside the data range, nor will any rules depend on the time of the last positive observation.
In these rules, ‘observation’ refers to any numeric measurement including zeros or negative values, but does not include missing or text values such as BQL.
Rules for interpolation:
If a start or end time occurs after the first observation and before the last observation but does not coincide with an observation time, then linear or logarithmic interpolation will be used to estimate the corresponding Y, according to the Calculation Method selected in the NCA Options. Note that logarithmic interpolation will necessarily be overridden by linear interpolation in the case of a non-positive endpoint.
If a start or end time occurs before the first observation but after the dose time, then the above rule still applies, and the interpolation will use the first observation and the value imputed at dose time (C0 for IV bolus dosing, zero for single-dose extravascular or IV infusion, Cmin/Ctau/Clast option for steady state, baseline for drug effect).
Rules for extrapolation:
If a start or end time occurs after the last numeric observation (after all observations even if Y is zero), and if Lambda_z is estimable, then the Lambda_z_intercept and Lambda_z values calculated for the terminal slope will be used to extrapolate the Y-value:
Y = exp(Lambda_z_intercept – Lambda_z * t)
= exp(Lambda_z_intercept – Lambda_z * Tlast) * exp(–Lambda_z * (t – Tlast))
= (predicted concentration at Tlast) * exp(–Lambda_z * (t – Tlast))
If a start or end time occurs after the last numeric observation and Lambda_z is not estimable, then the partial area will not be calculated.
Rules for AUC:
Each partial area time range will be divided into time segments based on the dataset’s observation times and the start and end times of the partial area. The linear or logarithmic trapezoidal rule will be used to compute the AUC for each time segment that ends before or at the last positive observation (Tlast), according to the Calculation Method selected in the NCA Options. Note that the logarithmic trapezoidal rule will be overridden by the linear trapezoidal rule if a Y-value for a time segment is non-positive or if the Y-values are equal.
If part or all of the partial area time range is at or after the last positive observation (Tlast), then the log-trapezoidal rule will be used after Tlast regardless of the Calculation Method selection. However, if non-positive observations occur after Tlast, then the logarithmic trapezoidal rule will necessarily be overridden by the linear trapezoidal rule.