See Anderson and Hauck (1983), or page 99 of Chow and Liu (2000). Briefly, the Anderson-Hauck test is based on the hypotheses:
H01: mT – mR < qL vs HA1: mT – mR > qL
H02: mT – mR < qU vs HA2: mT – mR > qU
where qL and qU are the natural logarithm of the Anderson-Hauck limits entered in the bioequivalence options tab. Rejection of both null hypotheses implies bioequivalence. The Anderson-Hauck test statistic is tAH given by:
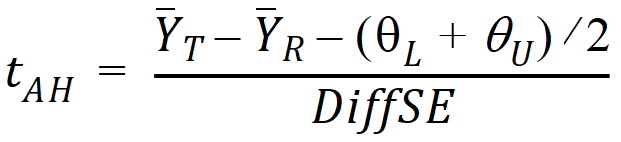
where DiffSE is the standard error of the difference in means. Under the null hypothesis, this test statistic has a noncentral t-distribution.