When the pharmacologic response takes time to develop and the observed response is not directly related to plasma concentrations of the drug a link model can be applied to relate the pharmacokinetics of the drug to its pharmacodynamics. Phoenix contains a group of indirect pharmacodynamic response (IPR) models proposed by Jusko (1990) and Dayneka, Garg, and Jusko (1993). The indirect response models differ from other models in Phoenix in that they use a PK model to predict concentrations, and then use these concentrations as input to the indirect PD response model.
Model 51: Inhibition of input.
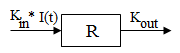
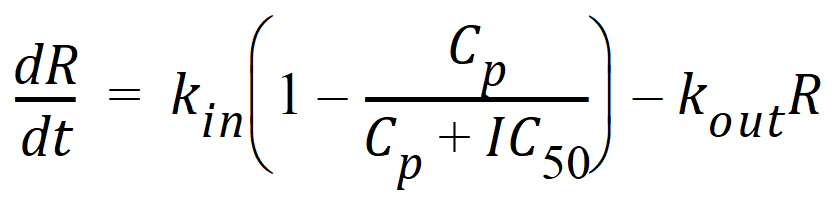
Estimated parameters: Kin Kout IC50
Model 52: Inhibition of output.
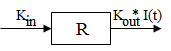
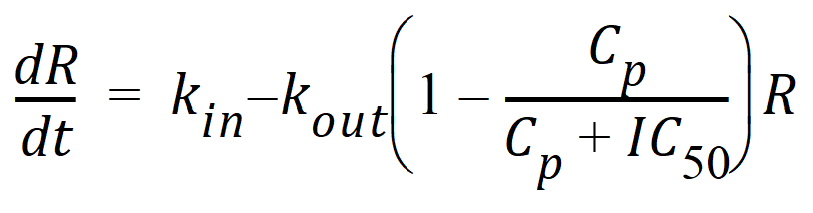
Estimated parameters: Kin Kout IC50
Model 53: Stimulation of input.

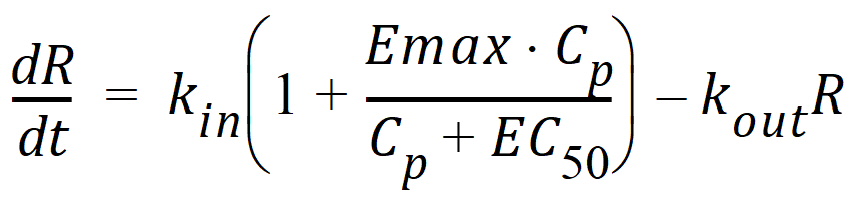
Estimated parameters: Kin Kout EC50 Emax
Model 54: Stimulation of output.
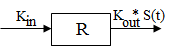
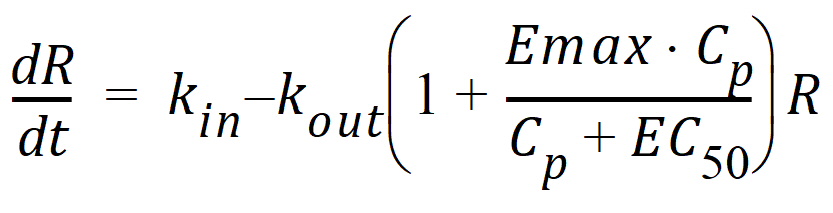
Estimated parameters: Kin Kout EC50 Emax
Model notation
R: Measured response to a drug.
kin: The zero-order constant for the production of response.
kout: The first-order rate constant for loss of response.
Cp: Plasma concentration of a drug.
Ce: Drug concentration at the effect site.
IC50: Drug concentration required to produce 50% of the maximal inhibition.
Emax: Maximum drug effect.
EC50: Concentration in plasma that achieves 50% of predicted maximum effect in an Emax model.