In determining the bioequivalence of a test formulation and a reference formulation, the first step is the computation of the least squares means (LSM) and standard errors of the test and reference formulations and the standard error of the difference of the test and reference least squares means. These quantities are computed by the same process that is used for the Linear Mixed Effects module. See the “Least squares means” section.
To simplify the notation for this and the following sections, let:
RefLSM: reference least squares mean,
TestLSM: test least squares mean,
fractionToDetect: (user-specified percent of reference to detect)/100,
DiffSE: standard error of the difference in LSM,
RatioSE: standard error of the ratio of the least squares means,
df: degrees of freedom for the difference in LSM.
The geometric LSM are computed for transformed data. For ln-transform or data already ln-transformed,
RefGeoLSM = exp(RefLSM)
TestGeoLSM = exp(TestLSM)
For log10-transform or data already log10-transformed,
RefGeoLSM = 10RefLSM
TestGeoLSM = 10TestLSM
The difference is the test LSM minus the reference LSM,
Difference = TestLSM – RefLSM
The ratio calculation depends on data transformation. For non-transformed,
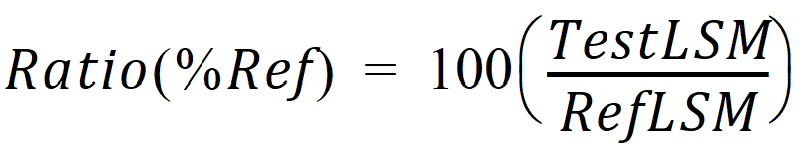
For ln-transform or data already ln-transformed, the ratio is obtained on arithmetic scale by exponentiating,
Ratio(%Ref) = 100exp(Difference)
Similarly for log10-transform or data already log10-transformed, the ratio is
Ratio(%Ref) = 100 x 10Difference