The following special functions (with some duplicates of the intrinsic versions, but with different names) are defined within the Phoenix PML language.
Link and inverse link functions
lnegbin_rp: logarithm of the probability mass function of a negative binomial, distribution parameterized by r and p, with its syntax given by lnegbin_rp(r, p, y)
megnin_rp: generate a random sample from a negative binomial distribution parameterized by r and p with its syntax given by rnegbin_rp(r, p)
lnegbin: logarithm of the probability mass function of a negative binomial distribution parameterized by mean, beta (=log(alpha)), and power with its syntax given by lnegbin(mean, beta, power, y)
pnegbin: probability mass function of a negative binomial distribution parameterized by mean, beta (= log(alpha)), and power (see “Count statement for Count models” for details) with its syntax given by pnegbin(mean, beta, power, y)
rnegbin: generate a random sample from a negative binomial distribution parameterized by mean beta (= log(alpha)), and power with its syntax given by rnegbin(mean, beta, power)
lpois: logarithm of the probability mass function of a Poisson distribution with its syntax given by lpois(mean, n), which returns the value of log(mean^n*exp(–mean)/n!).
ppois: probability mass function of a Poisson distribution with its syntax given by ppois(mean, n), which is the same as exp(lpois(mean, n)).
rpois: generate a random sample from a Poisson distribution (e.g., rpois(lambda) returns a random sample from a Poisson distribution with mean being lambda).
unifToPoisson: convert a uniform random number between 0 and 1 to a Poisson random number with its syntax given by unifToPoisson(mean, r), where mean denotes the mean of the Poisson distribution and r is the uniform random number.
lnorm: logarithm of the probability density function (PDF) of a normal distribution with mean being 0.
Its syntax is given by lnorm(x, std), where std denotes the standard deviation for the normal distribution.
lphi: logarithm of the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a normal distribution with mean being 0. Its syntax is given by lphi(x, v), where std denotes the standard deviation of the normal distribution.
phi: the CDF of the standard normal distribution with syntax given by phi(x).
dinvgauss: the PDF of an inverse Gaussian distribution parameterized by mean m and shape parameter n
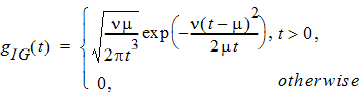
with its syntax given by dinvgauss(t, mean, shape).
ldinvgauss: logarithm of the PDF of an inverse Gaussian distribution parameterized by mean m and shape parameter n with its syntax given by ldinvgauss(t, mean, shape); that is, ldinvgauss(t, mean, shape) = log(dinvgauss(t, mean, shape).
pinvgauss: the CDF of an inverse Gaussian distribution parameterized by mean m and shape parameter n
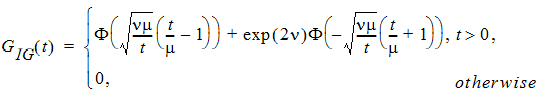
with a syntax given by pinvgauss(t, mean, shape). Here F denotes the CDF of the standard normal distribution.
lpinvgauss: the logarithm of the CDF of an inverse Gaussian distribution parameterized by mean m and shape parameter n with its syntax given by lpinvgauss(t, mean, shape). That is, lpinvgauss(t, mean, shape) = log(pinvgauss(t, mean, shape)).
dweibull: the PDF of a Weibull distribution parameterized by the shape parameter n and the scale parameter l
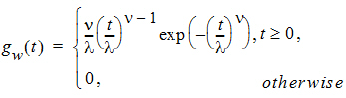
with its syntax given by dweibull(x, shape, scale).
ldweibull: the logarithm of the PDF of a Weibull distribution parameterized by the shape parameter n and the scale parameter l with its syntax given by ldweibull(x, shape, scale). That is, ldweibull(x, shape, scale) = log(dweibull(x, shape, scale)).
pweibull: the CDF of a Weibull distribution parameterized by the shape parameter n and the scale parameter l
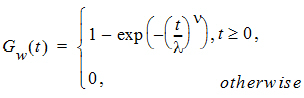
with its syntax given by pweibull(x, shape, scale).
lpweibull: logarithm of the CDF of a Weibull distribution parameterized by the shape parameter n and the scale parameter l with its syntax given by lpweibull(x, shape, scale). That is, lpweibull(x, shape, scale) = log(pweibull(x, shape, scale)).
Link and inverse link functions
probit: inverse of the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution with syntax given by probit(p).
iprobit: inverse probit with syntax given by iprobit(x), which is the same as phi(x).
ilogit: inverse-logit with syntax given by ilogit(x), which is equal to exp(x)/(exp(x)+1).
iloglog: inverse log-log link function with syntax given by iloglog(x).
icloglog: inverse complementary log-log link function with syntax given by icloglog(x).
CalcTMax: obtain Tmax for a macro-parameter model (e.g., CalcTMax(A, a, B, b, C, c)).
lambertw: the Lambert W-function is the inverse of function x given by x(y)=y*exp(y).
lgamm: logarithm of the gamma function (e.g., lgamm(x)).
factorial: factorial function (e.g., factorial(x) returns x factorial, and is the same as x!=x*(x – 1)*…*1).
erfunc: error function (e.g., erfunc(x) returns the value of the error function at x).
abs: absolute (e.g., abs(x) return the absolute value of x).
min: minimum (e.g., min(x, y))
max: maximum (e.g., max(x, y))
log10: log base 10 (e.g., log10(x))
ln: natural log (e.g., ln(x))
vfwt: observation variance function with its syntax given by vfwt(f, p), which returns the value of max(0, f^(p/2).
