The Bootstrap run mode is only available for Population models. Bootstrap is a diagnostic tool for understanding the precision of estimates. The assumption is that the observations are independent between subjects. Bootstrap consists of running a series of model fits, each time using a random sampling, with replacement, from the original set of individuals.
For example, if a user has 100 subjects in the original study data, then the created datasets, or resamples, will also contain 100 subjects per each bootstrap run, with some subjects replicated more than once. Several bootstrap samples can be created and all of the samples are individually fitted to the original model in order to obtain a new set of estimated parameters for each sample. After all the samples have been fitted, the bootstrapped estimates are summarized and then outputted.
When setting up a bootstrap run, enter the number of samples to create (# samples). The number of samples requested can be a number from two to infinity, however, very large numbers, such as one million or higher, are discouraged because of memory limitations.
The user can optionally select up to three particular categorical covariates from the Stratify menus to stratify the samples. This will ensure that each unique value available for the selected stratification variable will be sampled equally for each Bootstrap run. For example, if a user stratifies the data by sex and the data has 100 subjects that are 50% male and 50% female, then each resampled dataset will have 50 males and 50 females. A maximum of three stratifications can be selected, and the order of the selected stratified variables specifies a nesting structure. (In cases where reset blocks are involved, only the first values of covariates in the first reset block are used.)
The maximum number of tries (max tries) option accepts numbers from 2 to 99. If a sample fails to converge, it is re-tried as many times as indicated with different random seeds, in an effort to get a full set of samples evaluated.
The Estimate initial model parameters option, when checked, causes Phoenix to first run a simple fit to the model and then take the final estimates of the simple run as initial estimates for all the bootstrap runs. Typically, this option is not needed, since fine-tuning of the parameter estimates is normally done by the user prior to the bootstrap run and can significantly increase the run time for some models. (Note: When checked, the final estimates of the simple run will be copied into the original model text/fields.)
The Seed option is in the Run Options tab, and it is used as an initial seed value for the random sampling. Each subsequent bootstrap sample will use a different seed. Phoenix adds 100 to the starting seed. If the Keep? option is selected then the same starting seed will be used for the next run. Otherwise, Phoenix assigns a random seed and bootstrap results might vary if they are executed twice.
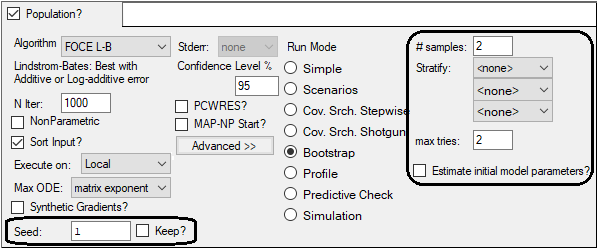
When running in Bootstrap mode, the Stderr option is disabled.
If scenarios are defined in the Scenarios tab using the covariate search methods or by manually creating them, then the scenario selected by the Use option button in the Scenarios tab is the one used for the Bootstrap procedure.
In the Fixed Effects tab, the Estimate area will automatically show the final bootstrap parameter estimates (means) after the Bootstrap run of the model is successfully executed.
