When pharmacological effects are seen immediately and are directly related to the drug concentration, a pharmacodynamic model is applied to characterize the relationship between drug concentrations and effect. Phoenix includes the following PD models:
|
Model |
Description |
Effect at C=0 |
Effect at C=infinity |
|
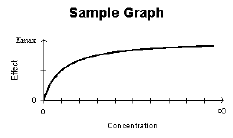
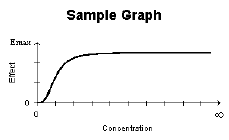
Simple Emax Model |
0 |
Emax |
|
|
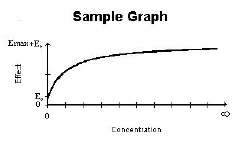
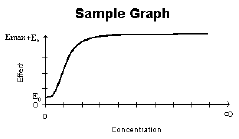
Simple Emax Model |
E0 |
Emax+E0 |
|
|
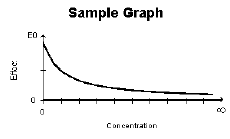
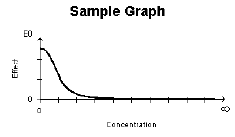
Inhibitory Effect E0 Model |
E0 |
0 |
|
|
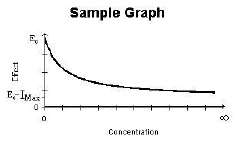
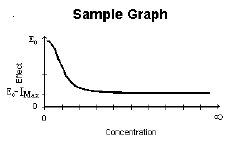
Inhibitory Effect Imax Model |
E0 |
E0 – Imax |
|
|
Sigmoid Emax Model |
0 |
Emax |
|
|
Sigmoid Emax Model |
E0 |
Emax+E0 |
|
|
Inhibitory Effect Sigmoid E0 Model |
E0 |
0 |
|
|
Inhibitory Effect Sigmoid Imax Model |
E0 |
E0 – Imax |
|
Term |
Definition |
|
Emax |
Maximum drug effect. |
|
Imax |
Maximum drug inhibition. |
|
E0 |
Baseline effect (effect at C=0). |
|
EC50 |
Concentration in plasma that achieves 50% of predicted maximum effect in an Emax model. |
|
IC50 |
Drug concentration required to produce 50% of the maximal inhibition. |
|
Rmax |
Effect at infinity (includes maximum drug effect/inhibition and baseline). |
|
F_Emax |
Fractional change in effect from baseline E0 |
|
Gamma |
Shape parameter |
Simple Emax model.
|
|
E=(Emax*C)/(C+EC50) |
Simple Emax model with a baseline effect parameter.
|
|
E=E0+(Emax*C)/(C+EC50) |
Inhibitory effect model.
|
|
E=E0*(1 – (C/(C+IC50))) |
Inhibitory effect model with a baseline effect parameter.
|
|
E=E0 – (Imax*C)/(C+IC50) |
Sigmoid Emax model.
|
|
E=(Emax*Cg)/(Cg+EC50g) |
Sigmoid Emax model with a baseline effect parameter.
|
|
E=E0+(Emax*Cy)/(Cg+EC50g) |
Sigmoid inhibitory effect model.
|
|
E=E0*(1 – (Cg/(Cg+IC50g))) |
Sigmoid inhibitory effect model with a baseline effect parameter.
|
|
E=E0 – (Imax*Cg)/(Cg+IC50g) |